Organization
The European Space Agency (ESA) is prime contractor for the Vega programme, which it manages from its ESRIN (European Space Research Institute) centre in Italy with an integrated team of staff from CNES and the Italian space agency ASI.
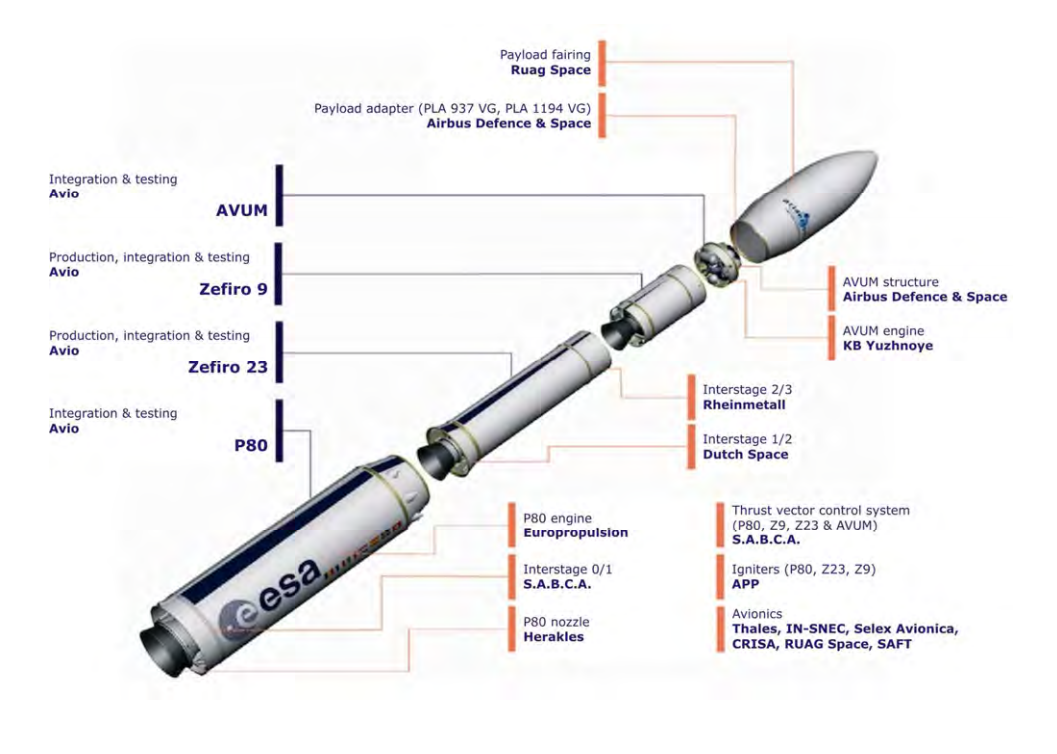
The member states contributing to ESA’s Vega programme vote its budgets and keep track of its progress. As programme leader, ESA proposes improvements and manages its joint funding. For the development of Vega and the P-80 booster, CNES, representing France, funded 25.3% of the budget of €710 million voted by governments to cover phases up to the maiden flight, and 24.1% of the budget for the VERTA (Vega Research and Technology Accompaniment) programme encompassing the launcher’s initial operating phase with five dedicated flights. While Vega is a European programme, it is often seen as an Italian one, since the Italian space agency ASI funded 50% of the budgets for its development and for VERTA, and Italian contractor Avio is a pivotal player, both directly and through its holdings in Spacelab S.P.A., Europropulsion and Regulus.
Vega final preparations and launch operations are performed at the Guiana Space Centre (CSG). The launch base belongs to CNES and its facilities are owned by ESA, which delegates responsibility for managing the launch pad to Arianespace and for Vega operations to Avio. Arianespace, based in Evry—in which ArianeGroup is the majority shareholder and Avio one of the minority shareholders—is the commercial operator of Vega.
Teams at CNES’s Launch Vehicles Directorate (DLA) provide their expertise in engineering, project management, quality assurance and RAMS (reliability, availability, maintainability, safety).
Crédits : Arianespace
